In an era where blockchain applications are predominantly accessed through desktop browsers and separate wallet extensions, the user experience often feels fragmented and distant from the seamless integration of modern mobile technology. Solana Labs, the organization behind the high-performance Solana blockchain, identified this chasm as a critical barrier to mainstream adoption. Their venture, Solana Mobile, is an ambitious initiative to merge the core principles of Web3—self-custody, user ownership, and decentralized applications (dApps)—with the ubiquity and convenience of a smartphone. Beginning with the limited-release Saga phone and now progressing to the highly anticipated, community-driven Chapter 2, Solana Mobile is not merely selling hardware; it is architecting an ecosystem. This article provides a neutral, in-depth analysis of the Solana Mobile project, examining the hardware evolution from Saga to Chapter 2, the foundational technology of the Solana Mobile Stack (SMS), its security model, and the broader implications for developers and users seeking a more integrated mobile Web3 experience.
Overview The Vision Behind Solana Mobile
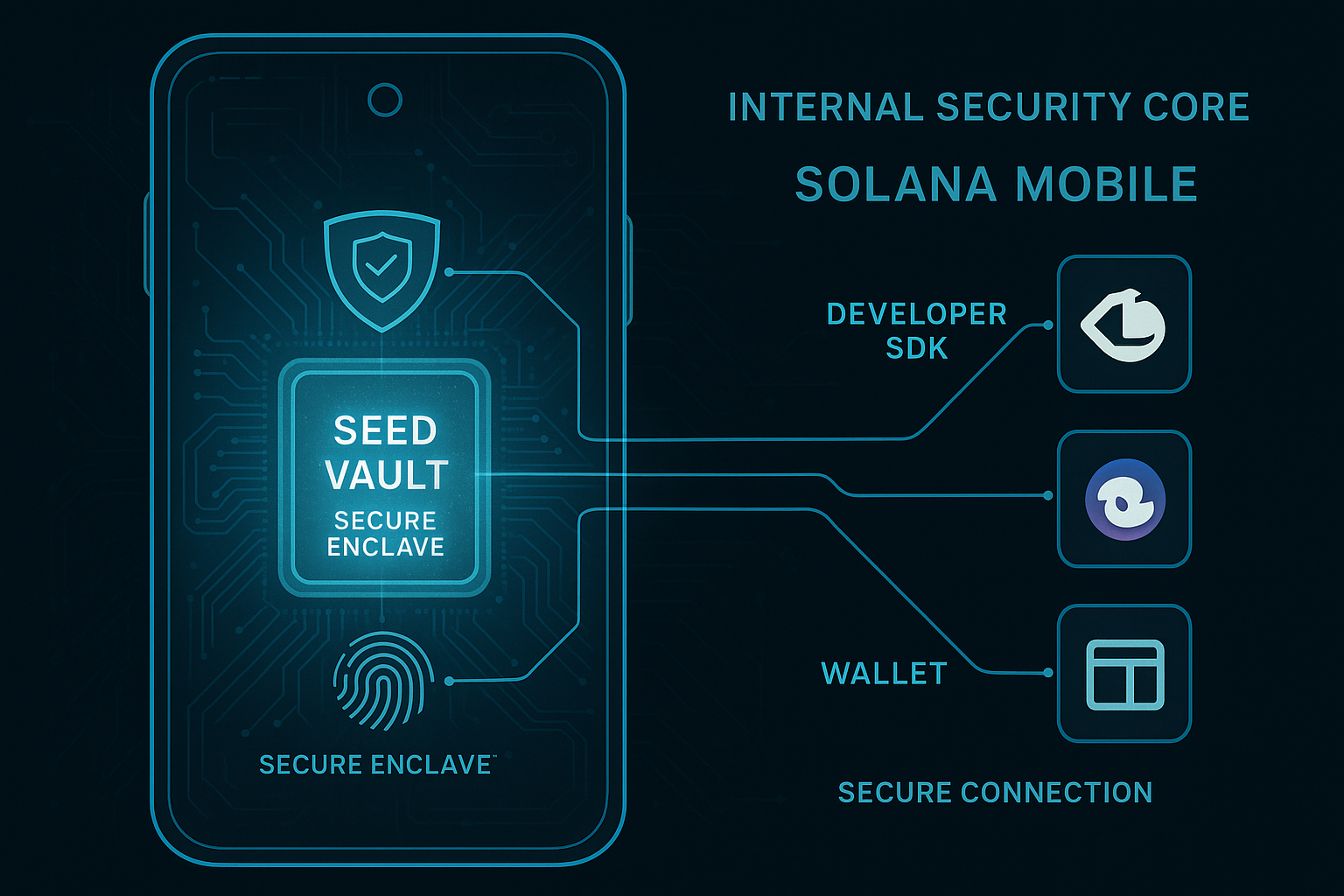
The foundational thesis of Solana Mobile is that for Web3 to reach a billion users, it must meet them where they already are: on their mobile devices. Traditional Web3 interactions require a complex dance of browser extensions, seed phrase management on insecure mediums, and constant app-switching, creating a significant UX hurdle. Solana Mobile’s vision is to abstract this complexity into a secure, intuitive, and natively integrated mobile operating system. Trading
This vision is built on two parallel tracks: the hardware, in the form of the Saga and Chapter 2 devices, and the software ecosystem, known as the Solana Mobile Stack (SMS). The hardware serves as a dedicated, optimized vessel for the SMS, providing the secure enclave necessary for true self-custody. The SMS, however, is designed to be portable. Its open-source nature means that, in theory, any Android manufacturer could integrate these Web3 primitives into their devices, potentially expanding the ecosystem far beyond Solana’s own branded phones. The goal is not necessarily to outsell Apple or Samsung but to establish a new standard for how blockchain is integrated into mobile operating systems, making secure, seamless Web3 access a baseline feature for future devices.
From Saga to Chapter 2 Design, Specs, and Hardware Upgrades

The journey of Solana Mobile hardware began with the Saga, a device that repurposed the premium Android framework of the OSOM OV1. Its launch was a proof-of-concept, demonstrating that a secure, dApp-first phone was technically feasible.
Solana Mobile Saga: The Pioneer
-
Specs and Features: The Saga was built on a flagship-grade foundation for its time, featuring a Qualcomm Snapdragon 8+ Gen 1 processor, 12GB of RAM, 512GB of storage, and a 6.67-inch OLED display. It included a 50MP primary camera and a 16MP ultra-wide lens, positioning it as a competent Android device irrespective of its Web3 features.
-
Initial Reception and Pivot: Initially, the Solana Mobile phone price of $1000 and a limited market saw slow sales. However, a strategic shift, including a significant price reduction and the discovery of valuable BONK token airdrops that effectively made the phone “free,” led to a complete sell-out. This event highlighted a unique dynamic between hardware and token incentives within the Solana community.
Solana Mobile Chapter 2: The Community-Driven Successor
Learning from the Saga experience, Solana Mobile announced Chapter 2 with a different philosophy: lower the barrier to entry and build based on overwhelming community demand.
-
Release Date and Preorders: Announced in early 2024, the Solana Mobile Chapter 2 release date is anticipated for the first half of 2025. The device was opened for preorders with a $450 price point, dramatically lower than the Saga’s launch price. The “how to preorder Solana Mobile” process was simplified through its official website, requiring a refundable deposit. The overwhelming response—exceeding 100,000 preorders in weeks—signaled strong market appetite for a more accessible Web3-native device.
-
Anticipated Specs and Features: While final Solana Mobile specs and features for Chapter 2 are subject to change, it is expected to utilize a mid-tier chipset like the Snapdragon 8s Gen 3, balancing performance and cost. The focus is less on competing with the absolute best camera systems and more on delivering a smooth, reliable experience for the core use case: running dApps, managing assets, and engaging with the Solana ecosystem. Improvements in Solana Mobile battery life and general thermal management are also anticipated based on community feedback from the Saga.
When conducting a Solana Mobile vs iPhone or Solana Mobile vs Android flagships analysis, it’s crucial to understand the different value propositions. An iPhone 15 Pro or a Samsung Galaxy S24 excels as a general-purpose consumer device with a vast, polished app ecosystem. The Solana Mobile devices, however, are specialized tools optimized for a specific, growing niche. Their value is intrinsically linked to the utility of the Solana Mobile Stack and the dApp store, not just raw hardware specifications.
Solana Mobile Stack (SMS) The Core Technology and SDK Features
The true innovation of Solana Mobile lies not in the handset itself, but in the open-source software framework that powers it: the Solana Mobile Stack (SMS). The SMS is a collection of libraries, standards, and tools that enable developers to build rich Web3 experiences for Android.
Key components of the SMS include:
-
Mobile Wallet Adapter (MWA): This is the communication protocol that allows dApps to securely interact with wallets on the device. It standardizes the connection, eliminating the need for dApp developers to write custom code for every wallet. For users, this means a consistent, secure signing experience regardless of the dApp they are using.
-
Seed Vault: Detailed in the next section, this is the secure execution environment that houses private keys.
-
Solana Pay for Mobile: A set of APIs that make it simple to integrate QR-code-based payment flows directly into mobile dApps, enabling seamless point-of-sale and peer-to-peer transactions.
-
dApp Store: A curated marketplace for Android applications that leverage the SMS, providing a primary distribution channel for Web3 mobile apps outside of the traditional Google Play Store.
The Solana Mobile Stack (SMS) guide for developers emphasizes security and simplicity. By providing a standardized SDK, Solana Mobile reduces the friction for Web3 developers to port their existing dApps or build new mobile-first experiences, knowing that key management and transaction signing will be handled securely and consistently by the SMS.
The Seed Vault Hardware-Backed Security and Key Management
At the heart of the Solana Mobile security model is the Seed Vault, a secure system process that operates in an isolated environment on the device. This is the cornerstone of self-custody best practices on mobile.
The Seed Vault functions as a dedicated, protected space where a user’s private keys are generated, stored, and used for signing transactions. It is designed to be inaccessible to other apps and the main Android operating system, significantly reducing the attack surface for malware or phishing attempts.
klik At Here Too Read More About MEXQuick News
Key features include:
-
Hardware-Backed Keys: The Seed Vault leverages the device’s hardware-level security, such as the Android Keystore, to ensure that keys cannot be extracted, even with root access.
-
Biometric Authentication: Every transaction signing request is gated by user approval via fingerprint or facial recognition. This adds a critical layer of confirmation, ensuring that no transaction can be executed without explicit user consent.
-
Seamless dApp Interaction: When a user interacts with a dApp that uses the Mobile Wallet Adapter, the transaction request is passed to the Seed Vault. The user authenticates, reviews the transaction, and signs it—all within the secure environment. The signed transaction is then passed back to the dApp, which never has direct access to the private key.
This architecture makes the process of installing dapps on Solana Mobile inherently safer than on a standard Android device. The Solana Mobile seed vault setup is a one-time process during device initialization, guiding the user to securely back up their recovery phrase. This approach effectively brings the security standards of a hardware wallet into the form factor of a daily-driver smartphone.
dApp Store and Web3 Experience How Users Discover and Use dApps
A critical differentiator for Solana Mobile is its integrated Solana Mobile dapp store. This is a sideloaded Android store that bypasses the restrictions of the Google Play Store, allowing for the distribution of applications that incorporate native crypto-economic features, such as integrated token swaps or NFT minting, which are often against the policies of mainstream app stores.
For users, this provides a centralized hub for dApp discovery on mobile. The store is curated, which helps to mitigate the risk of scam applications, a significant problem in the open Web3 space. Users can find a wide range of applications, from decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and NFT marketplaces to gaming and social media dApps, all optimized for the Solana Mobile experience.
The user flow for engaging with these dApps is streamlined. For example, the NFT minting flow on a Solana Mobile device is significantly smoother than on a desktop. A user can browse an NFT project in the dApp Store, tap “Mint,” and be presented with a clear transaction request from the Seed Vault. After biometric authentication, the transaction is signed, and the NFT arrives in their integrated wallet. This eliminates the need for connecting a wallet, switching between tabs, or confirming multiple pop-ups, creating a user experience that rivals Web2 applications in its simplicity.
Wallet Integrations Phantom, Solflare, and Solana Pay
While the Seed Vault manages the keys, wallet applications provide the user interface for managing assets, viewing NFT collections, and connecting to dApps. The Solana Mobile ecosystem has seen robust adoption from major wallet providers.
Phantom wallet on Solana Mobile and Solflare wallet on Solana Mobile are the two leading wallet interfaces for the platform. These apps are specially built to interface with the Seed Vault via the Mobile Wallet Adapter. When a user opens Phantom on their Saga phone, the app is not managing its own private keys. Instead, it acts as a view into the assets controlled by the keys securely stored in the Seed Vault. All transaction signing is delegated to the Vault. This separation of concerns—where the wallet is a view and the Vault is the secure signer—enhances security and provides a consistent experience across all dApps.
Solana Pay on Solana Mobile is another killer feature. This open protocol for token payments leverages QR codes for instant, fee-free transactions. On a Solana Mobile device, a user can simply open their wallet, scan a Solana Pay QR code from a merchant, and confirm the payment with their fingerprint. The transaction is broadcast directly from the phone. This integration positions the device as a potent tool for real-world commerce, bridging the gap between digital asset ownership and physical point-of-sale interactions. Trading
For Developers SDK, Mobile Wallet Adapter, and Grant Opportunities
The success of the Solana Mobile ecosystem hinges on developer adoption. To this end, Solana Labs has provided comprehensive resources and incentives.
The primary tool is the Solana Mobile SDK, which includes the Mobile Wallet Adapter, making it straightforward for any existing Solana dApp to become mobile-compatible. A Solana Mobile SDK tutorial would typically show a developer how to integrate the MWA library, which automatically handles the connection to any SMS-compatible wallet on the device. This means a developer writes their connection logic once, and it works seamlessly with Phantom, Solflare, and any future wallet that adheres to the standard.
Beyond the SDK, the Solana developer grants program and the community builders program actively fund and support projects building mobile-first dApps. This financial and technical support is crucial for fostering a vibrant marketplace for mobile-first dApps. The focus is on applications that leverage the unique capabilities of mobile devices and the SMS, such as location-based services, enhanced camera integration for AR and NFTs, and the seamless UX provided by the Seed Vault.
Solana Mobile vs Traditional Smartphones Performance and Privacy
A direct comparison between Solana Mobile devices and traditional smartphones requires a nuanced perspective on performance and privacy.
In terms of raw computational power, a flagship Android device or iPhone will likely outperform the Saga and certainly the Chapter 2 on standard benchmarks and tasks like video editing or high-frame-rate gaming. However, for the specific task of interacting with the Solana blockchain—signing transactions, querying RPCs, and rendering dApp interfaces—the Solana Mobile devices are highly optimized. The integrated stack reduces RPC latency and provides a more fluid Web3-specific experience.
The privacy and data ownership model is fundamentally different. Traditional smartphones and app stores are part of an ecosystem where user data is a primary product. In the Solana Mobile model, the user retains ownership of their assets and data. Transactions are peer-to-peer and recorded on a public ledger, but personal identity is not inherently tied to wallet addresses. The Solana Mobile security review of its architecture shows a design that prioritizes user sovereignty over the data-collection models prevalent in Web2.
User Feedback, Community, and Ecosystem Adoption
The Solana Mobile user reviews from the Saga community have been instrumental in shaping the Chapter 2. Early adopters praised the seamless dApp integration and the security of the Seed Vault but also provided critical feedback on hardware aspects like battery life and the initial scarcity of high-quality dApps. The massive pre-order numbers for Chapter 2 demonstrate that the core value proposition resonates strongly, despite the first-generation hardware’s imperfections.
Ecosystem adoption is growing. The success of the Saga, driven in part by Solana Mobile airdrop eligibility for various projects, created a powerful flywheel. Projects now actively develop for the Solana Mobile platform to engage with this dedicated and economically active user base. This has accelerated the growth of the dApp Store, creating a more valuable ecosystem for all users. Regular Solana Mobile software updates have also shown a commitment to iterating and improving the software experience based on this user feedback.
The Future of Solana Mobile Chapter 2, Airdrops, and Developer Roadmap
The future trajectory of Solana Mobile is multi-faceted, centered on the successful launch of Chapter 2 and the continued expansion of the SMS ecosystem. The Solana Mobile Chapter 2 launch in 2025 will be a critical test of its ability to scale from a niche developer device to a mainstream-adjacent product. Managing the supply chain for over 100,000 units is a significant challenge. The community is also highly anticipating the Solana News Mobile airdrop eligibility that may come with the new device, mirroring the Saga experience, though this should be viewed as a potential ecosystem perk rather a guaranteed financial return.
The developer roadmap will likely focus on enhancing the SMS with more advanced features, such as deeper integration with blinks (blockchain links) and actions, which allow any Twitter/X link to become an interactive transaction. Improvements in account abstraction could further simplify the user experience by enabling features like social recovery or sponsored transactions. The long-term goal remains clear: to make the Solana Mobile Stack the de facto standard for secure Web3 on Android, whether on a Solana-branded device or through partnerships with other manufacturers.
Closing Section
Solana Mobile represents a bold and technically sophisticated experiment in bridging the worlds of blockchain and mobile technology. It moves beyond the concept of a simple “crypto phone” by building a comprehensive, open-source stack—the Solana Mobile Stack—that integrates deeply with Android to provide a secure and user-friendly Web3 environment. The Seed Vault brings hardware-wallet-level security to a smartphone, while the dApp Store and Mobile Wallet Adapter create a cohesive ecosystem for developers and users alike. While the hardware, from the pioneering Saga to the upcoming Chapter 2, serves as the physical vessel, it is the software and the growing community of builders that form the true core of this initiative. By focusing on education, developer tools, and a seamless user experience rather than speculative value, Solana’s mobile initiative may indeed redefine how Web3 meets mainstream mobile devices, making self-custody and decentralized applications an accessible reality in the user’s pocket.

